Szabla, R.; Góra, R. W.; Janicki, M.; Sponer, J. Faraday Discuss. 2016 DOI: 10.1039/C6FD00131A
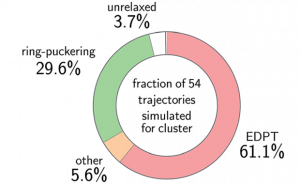 Non-adiabatic molecular dynamics simulations and potential energy surface calculations of the photoexcited imidazole–(H2O)5 cluster using the ADC(2) Hamiltonian indicate that electron driven proton transfer (EDPT) along a wire of at least two water molecules may lead to the formation of a πσ*/S0 state crossing, similarly to what we suggested for 2-aminooxazole. To embed the results in a biological context, we provide calculations of potential energy surface cuts for the analogous photorelaxation mechanism present in adenine, which contains an imidazole ring in its structure.
Non-adiabatic molecular dynamics simulations and potential energy surface calculations of the photoexcited imidazole–(H2O)5 cluster using the ADC(2) Hamiltonian indicate that electron driven proton transfer (EDPT) along a wire of at least two water molecules may lead to the formation of a πσ*/S0 state crossing, similarly to what we suggested for 2-aminooxazole. To embed the results in a biological context, we provide calculations of potential energy surface cuts for the analogous photorelaxation mechanism present in adenine, which contains an imidazole ring in its structure.